
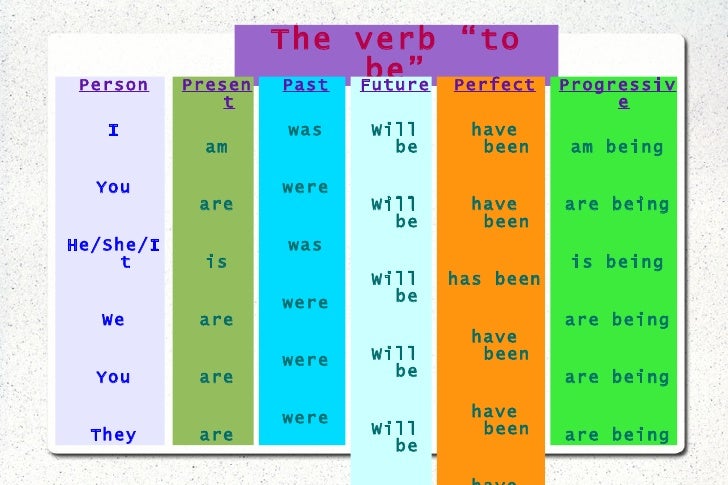
Sentences in the past perfect tense and the past perfect progressive tense use "had" along with the main verb, no matter whether the subject is singular or plural. Singular present perfect progressive - Both dogs have been barking for hours.Singular present perfect progressive - The dog has been barking for hours.Plural present perfect - Her friends have graduated from college.Singular present perfect - She has graduated from college.In the present perfect tense and the present perfect progressive tense, the verb "to have" must match the singular or plural subject: Plural past progressive - The cars were working yesterday.Singular past progressive - The car was working yesterday.
Plural present progressive - His brothers are running in a marathon.Learn more about these verbs with this helpful chart of samples. Singular present progressive - Peter is running in a marathon. Sometimes the best way to understand what singular and plural verbs are is to see examples.For example, in the progressive tenses, the verb "to be" changes with the subject: When you're writing in the progressive or perfect tenses, the main verb doesn't change with singular or plural subjects - but the linking verb does. Plural irregular - They sold my motorcycle.Singular irregular - He sold my motorcycle.Plural irregular - We came to the party.Singular irregular - She came to the party.Plural regular - Dave and Miles played football.Singular regular - Dave played football.Plural regular - The neighbors helped me.Regular past tense verbs (and most irregular past tense verbs) are the same for both singular and plural subjects. Deciding whether a verb is plural or singular mostly happens when you're writing in the present tense.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
